Study Guide
Field 020: Earth/Space Science
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
Subarea 1—FOUNDATIONS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY
Objective 002
Apply knowledge of materials, methods, and equipment commonly used in earth/space science.
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used in the study of the earth and space sciences primarily to:
- determine an observer's precise location on the earth using satellite data.
- examine and display spatial relationships between related data sets.
- gather data from the earth's surface using remote sensing techniques.
- analyze maps made by cartographers prior to computerization of mapping.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 003
Understand the nature and history of scientific thought and inquiry.
2. Use the passage below to answer the question that follows.
The theory of catastrophism, developed in the seventeenth century, stated that the earth's landscape was formed by catastrophic events. Supporters of the theory thought the Noachian flood described in the Bible was the most recent of these events, and that different layers of rock represented different precipitates that formed as the ocean receded.
The articulation of the theory of catastrophism helped advance the development of scientific knowledge because it:
- promoted research into the structural differences and properties of different rock types.
- supplied a unifying theory that made a coherent whole from scientific and biblical knowledge.
- defined the scope of scientific inquiry by distinguishing between the knowable and the unknowable.
- provided a hypothesis that could be validated or rejected as researchers collected and analyzed new data.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D.
Objective 004
Understand the relationship of earth/space science to contemporary, historical, technological, and societal issues.
3. Lining of sanitary landfills with a clay barrier is most useful for which of the following purposes?
- to reduce the surfacing of methane and other gases
- to minimize bacterial interaction with the waste
- to speed the rate of biodegradation of waste
- to prevent leachate from migrating away from the waste site
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D.
Objective 005
Demonstrate knowledge of the interrelationships among the life, physical, and earth/space sciences and among science, mathematics, and technology.
4. Mathematics is understood to be the language of science primarily because it:
- has no cultural bias associated with its practice.
- describes predictable and testable relationships.
- reduces the uncertainty associated with chaotic systems.
- relies on the same processes as science.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Subarea 2—PHYSICAL AND HISTORICAL GEOLOGY
Objective 006
Demonstrate knowledge of the structure, characteristics, and processes of the earth.
5. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
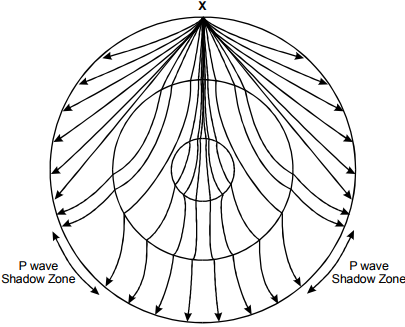
The diagram represents the earth as three concentric circles for the inner core, the outer core, and the outer mantle. Point X is located at the top of the diagram, on the surface of the earth. Dozens of lines, representing P lines from an earthquake at point X, radiate from point X in all directions through the earth. P waves that do not pass through the outer or inner core regions continue in a straight line. P waves that pass through the outer and inner cores are deflected toward the diagram's center line each time they pass from one region to the next, resulting in a series of arcs. Lines that pass through the outer portion of the outer core cluster toward the lines that traveled in a straight path, while lines that pass closer to the center line of the diagram cluster toward the bottom of the diagram. This creates areas on the surface, roughly between 30 and 60 degrees below the horizontal axis on each side, where no P waves resurface. Each of these is labeled "P wave Shadow Zone."
The diagram above shows the earth's crust and the boundaries of the earth's outer and inner cores. Propagation pathways of P waves recorded after an earthquake located at position X are shown as lines radiating out from position X. Which of the following best explains the P wave shadow zones indicated on the diagram?
- the reflection of seismic waves as they encounter the differing densities of the inner and outer cores
- the variable absorption of seismic waves as they pass through the mantle and the outer and inner cores
- the refraction of seismic waves as they cross boundaries between materials with different densities
- the differing speed of seismic waves moving into the increasingly dense materials of the outer and inner cores
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Objective 008
Understand processes and consequences of weathering, erosion, and deposition.
6. Which of the following best describes the geologic event that produced the flat, rich agricultural lands surrounding Saginaw Bay along the east shore of Michigan's Lower Peninsula?
- weathering of glacial till
- deposition of wind blown fine sand and silt
- isostatic uplift of a former lake bed
- erosion of underlying Precambrian shale strata
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Objective 009
Demonstrate knowledge of the geologic time scale and the methods of relative and absolute dating.
7. Use the block diagram below to answer the question that follows.
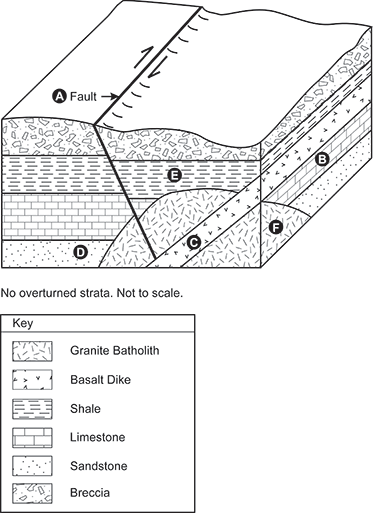
The block diagram shows a cross-section of several geological strata. According to the key, the basic layers are, from top to bottom, breccia, shale, which is labeled E, limestone, which is labeled B, and sandstone, which is labeled D. There is a granite batholith, labeled F, that extends from the lower right corner up as far as the layer of shale. There is a basalt dike, labeled C, that slants from the center front, up and to the right, to extend into the layer of shale. There is a fault, labeled A, that slants from the upper left down through the layers of breccia, shale, and limestone, and the granite batholith, ending at the basalt dike. To the right of the basalt dike, the batholith and rock layers are shifted slightly lower than to the left of the dike.
In the geologic block diagram shown above some of the strata are labeled with the letters B, C, D, E, and F. The fault is labeled as A. Which of the following best reflects the sequence of deposits from oldest to most recent and the timing of faulting?
- E, B, D, F, A, C
- D, B, E, F, A, C
- F, D, B, E, A, C
- D, B, E, A, F, C
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 010
Understand the formation and use of geologic resources, and the relationship between the geosphere and human activities.
8. The cation-exchange capacity of a particular type of soil is an important characteristic of the soil. This is primarily because the cation-exchange capacity of a soil:
- affects the rate of nutrient leaching from the topsoil.
- regulates the release of nutrients from the surface litter.
- accelerates the breakdown of minerals into available nutrients.
- determines the nutrients that are available to soil microorganisms.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A.
Subarea 3—OCEANOGRAPHY AND FRESHWATER SYSTEMS
Objective 011
Demonstrate knowledge of the physical components and processes of the marine system.
9. Which of the following best describes the pelagic zone of the marine environment?
- upper layers of the open ocean where photosynthesis can occur
- ocean-bottom surfaces with enough sunlight to support photosynthesis
- open oceans regardless of their depth or location
- ocean-bottom surfaces regardless of their location or topography
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Objective 012
Understand the distribution of freshwater and the processes involved in the hydrologic cycle.
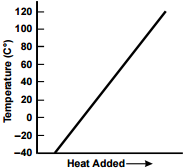
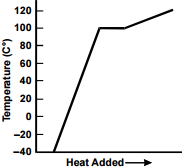
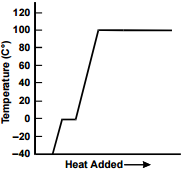
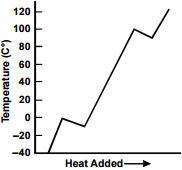
10. A sample of ice at –40º C is heated in an open vessel. Which of the following charts best represents the relationship between heat added and the temperature of the sample?
Each response is a line graph with a single data line. The vertical axis is labeled "Temperature (C°)," with values marked from negative 40 to 120 in increments of 20. The horizontal axis is labeled "Heat Added" with an arrow to the right.
The data line extends in a single straight segment from the horizontal axis upward to the upper right, to at least 120 C°.
The data line extends from the horizontal axis upward to about 100 C°, remains horizontal for a short distance, then continues at a shallower slope to at least 120 C°.
The data line extends from the horizontal axis upward to about 0 C°, remains horizontal for a short distance, then continues to about 100 C°, then remains horizontal.
The data line extends from the horizontal axis upward to about 0 C°, slopes slightly down to about negative 10 C°, continues upward to about 100 C°, slopes slightly down to about 90 C°, then continues to at least 120 C°.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Objective 013
Apply knowledge of groundwater.
11. A community gets its water from aquifers located in limestone strata. Which of the following is likely to characterize the water derived from these aquifers?
- exceptional clarity due to effective filtration
- high levels of dissolved calcium carbonate
- cloudiness due to the presence of organic solids
- strong odor and flavor of sulfur
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 015
Understand the relationship between the hydrosphere and human activity.
12. Following the completion of the Aswan High Dam on the Nile River in Egypt, the annual harvest of marine fish species decreased in the region surrounding the Nile Delta. The decrease in fish stocks in this part of the Mediterranean Sea was most likely related to a change in:
- dissolved oxygen levels.
- salt concentration.
- water clarity.
- nutrient availability.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D.
Subarea 4—METEOROLOGY
Objective 017
Understand the formation of clouds, precipitation, and condensation.
13. Which of the following is a necessary condition for condensation to occur in the atmosphere?
- a rapid increase in the concentration of water vapor
- the presence of microscopic particles
- a relative humidity slightly over 100 percent
- the existence of significant contrasts in temperature across the region
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 018
Understand the causes of different kinds of weather.
14. Which of the following best explains why hurricanes typically do not form on the equator?
- The Coriolis force, which is critical in supporting large-scale rotation in developing hurricanes, is zero at the equator.
- The upper-level winds on the equator are strongest during the summer season, disrupting the vertical growth of tropical storms.
- The sinking of convergent air flows that meet at the equator creates a high pressure zone not conducive to hurricane growth.
- Upwelling currents keep ocean surface temperatures at the equator below 80 degrees, which is too cool to support hurricane development.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A.
Objective 019
Apply knowledge of the earth's climate systems and analyze the factors that influence climate.
15. Scientists now realize that the El Niño / Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon affects climates worldwide. Which of the following best describes a predictable climate change in Michigan during a year with a strong El Niño pattern?
- below-average summer and fall temperatures
- above-average fall and winter precipitation
- below-average winter and spring precipitation
- above-average fall and winter temperatures
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D.
Objective 020
Understand the relationship between the atmosphere and human activity.
16. Since 1977, scrubbers have been required for the exhaust fumes of all new fossil-fuel-burning power plants and smelters. These devices are used to reduce emissions of:
- carbon dioxide.
- lead and other heavy metals.
- sulfur dioxide.
- volatile organic compounds.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Subarea 5—ASTRONOMY
Objective 021
Understand the characteristics of the sun-earth-moon system.
17. Which of the following best explains why typical sunrises and sunsets are often characterized by red-, yellow-, and orange-colored skies?
- The relative humidity tends to be higher in the atmosphere at those times of day, and water vapor preferentially absorbs visible light in the blue region of the spectrum.
- The low angle of the sun results in the light passing through a thicker atmosphere, and longer wavelengths are more likely to penetrate without being scattered.
- The higher concentration of particulate matter in the atmosphere at those times of day is more likely to scatter longer wavelengths across the sky than shorter wavelengths.
- The greater distance the sun's light travels to reach the earth results in the Doppler effect, shifting incident light toward the longer wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 022
Recognize the components of the solar system.
18. Over the course of several thousand years, the position of Polaris, the North Star, in the night sky has changed. This phenomenon is due to:
- the continuous rotation of the solar system.
- changes in the angle of the earth's orbital plane to the solar system.
- the continuous revolution of the Milky Way galaxy.
- changes in the orientation of the earth's rotational axis.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D.
Objective 023
Understand stellar evolution and the formation of the universe.
19. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
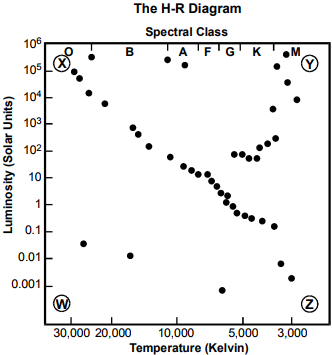
The information is a square plot titled "The H-R Diagram." The left side is labeled "Luminosity (Solar Units)," with values labeled from 0.001 to 10 to the sixth in increments of powers of 10. The bottom side is labeled "Temperature (Kelvin)," with value labels of 30,000, 20,000, 10,000, 5,000, and 3,000. The top side is labeled "Spectral Class," with sections labeled, from left to right, O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. In the lower left corner is a circled W. In the upper left corner is a circled X. In the upper right corner is a circled Y. In the lower right corner is a circled Z. There is a roughly linear pattern of dots from the X to the Z. There is a loose trail of dots that meanders from slightly above and to the right of the center of the chart upward toward the Y. There are a few dots scattered along the top edge. There are 3 dots scattered in the region between the W and the Z.
In the H-R diagram above, stars are plotted as dots based on their luminosity and spectral class or temperature. Near which of the following regions of the H-R diagram would a red giant most likely be located?
- near the W
- near the X
- near the Y
- near the Z
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Objective 024
Demonstrate knowledge of the history of astronomy.
20. Which of the following historical accomplishments provided the first convincing evidence that the earth and other planets orbited the sun?
- Copernicus's explanation for the retrograde motion of Mars
- Galileo's observation that Venus went through phases like the moon
- Aristotle's careful observations of planetary motions
- Tycho Brahe's observation that stars were outside the sphere of planets
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.